Use with GitLab
You can use GitLab with Coherence to streamline your development and deployment workflow. When you push changes to your GitLab repository, GitLab's pipeline builds your application and creates a Docker image. This image is then pushed to a cloud registry managed by Coherence, which deploys it to your specified environment.
This guide demonstrates the process by deploying a Flask application stored on GitLab to Coherence, using backend and database services.
Prerequisites
- A Coherence account.
- A GitLab account and repository with a Dockerfile. If you do not have one, you can clone our Coherence Flask example application.
- An Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Google Cloud Platform (GCP) account.
Set up Coherence
To set up the project in Coherence, you need to create an app, add a collection, and create an environment. If you're new to Coherence or need a refresher on these steps, refer to the quick start guide.
Create a service
Next, create a service in the environment. Enter all the details necessary for the service and choose the Existing Image option. A temporary image name is used at this stage because the app needs to be created and provisioned before Coherence provides the final image URI.
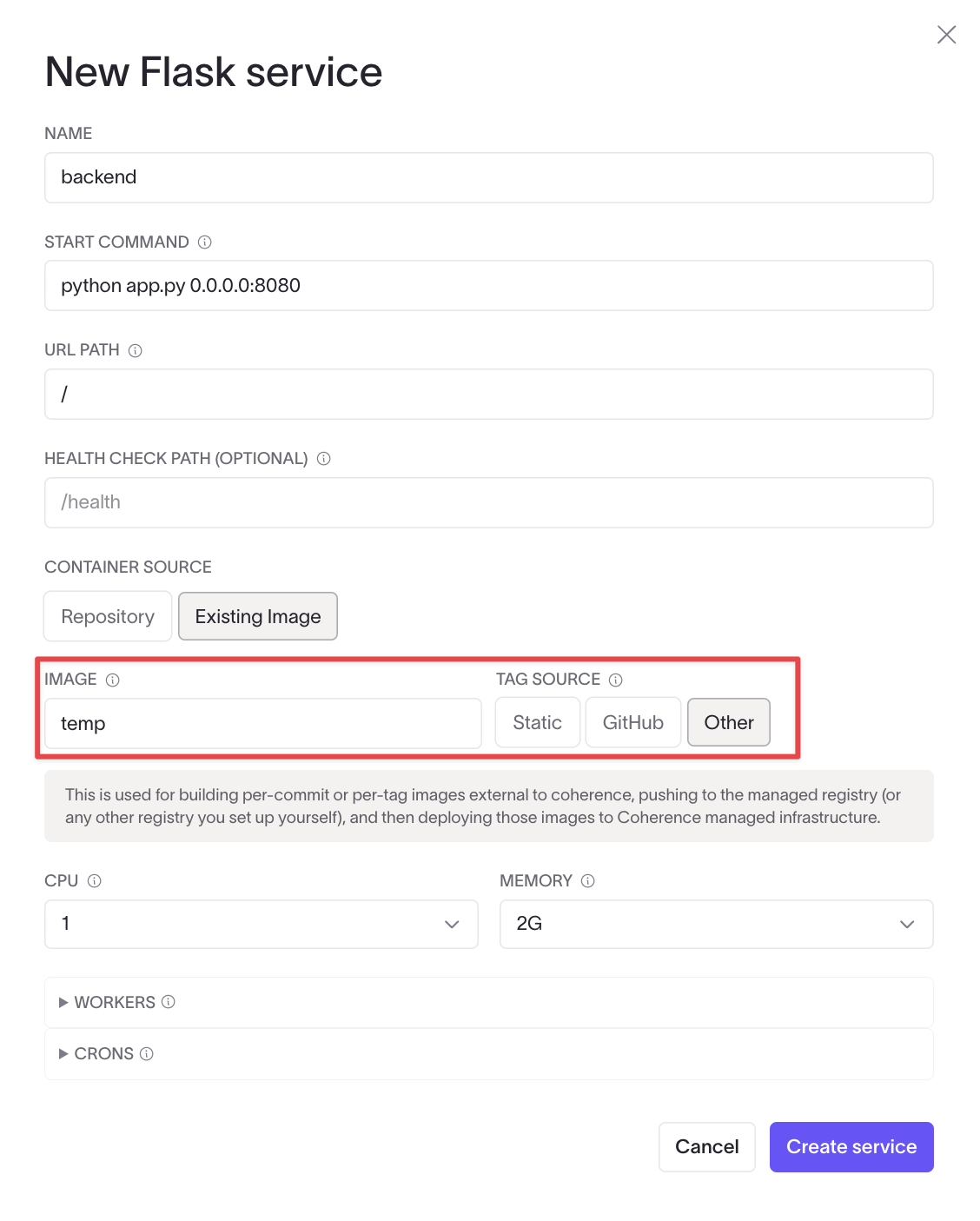
If you are following with the Flask example, create a database service, choose Postgres, and give it a name. Click Create service.
Set up IAM permissions
Follow the prompts on the dashboard to connect the app to a cloud account, then follow the on-screen instructions to set up the necessary IAM permissions.
Customize the cnc.yml file
Now you can customize the cnc.yml file to fine-tune your deployment configuration.
If you are following along with the example project, update the x-cnc configuration for the backend service to include a migrate command as shown below:
services:
backend:
...
x-cnc:
type: backend
system:
health_check: ''
migrate: flask db migrate -m "Initial migration."
url_path: /
...
Provision the app
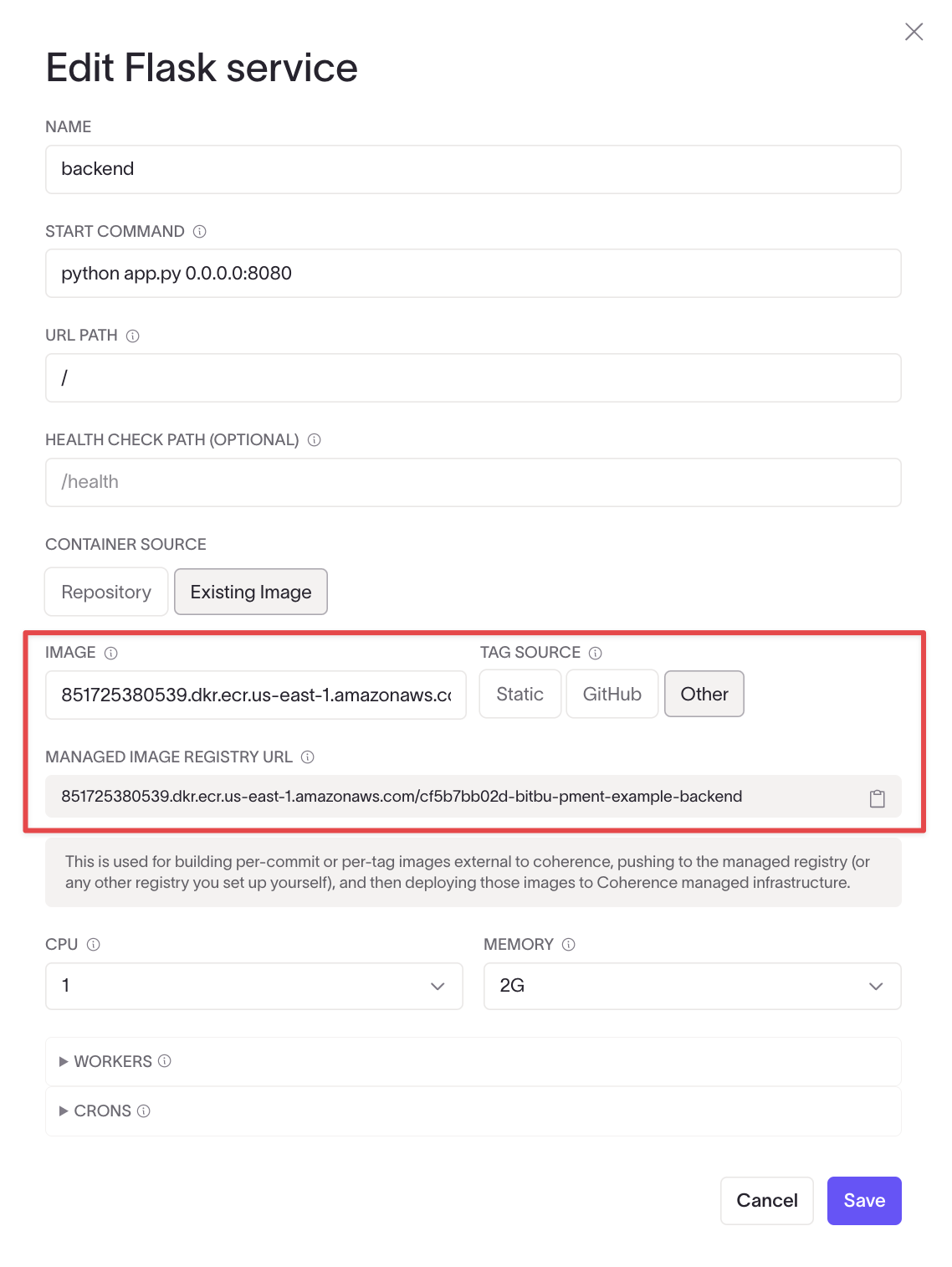
Once permissions are set, follow the prompts in the dashboard to provision the app infrastructure. When provisioning is complete, edit the service to find the managed registry URI. Replace the temporary name with the registry URI and press Save. Provision the app again.
Create an access token
The GitLab pipeline will need to authenticate cocli, the Coherence CLI.
Navigate to your profile on Coherence. In the API section, generate a new access token for the application. Save the value of this token for the GitLab pipeline setup.
Authenticate with the cloud service
GitLab pipelines need authentication keys to interact with your cloud service. The process differs depending on whether you're using Google Cloud or AWS. Follow the instructions for your chosen cloud provider:
In the Google Cloud console, navigate to IAM & Admin > Service Accounts. Click on Create Service Account at the top of the page. Follow the on-screen prompts and ensure that the permissions are set to include at least the Artifact Registry Service Agent.
In the service account details page, go to the Keys tab, click Add Key, and choose Create new key. Select JSON as the key type and click Create. This will generate and download a new key file in JSON format.
Once you have the key file downloaded, encode it on your machine using the following command:
cat your-service-account-key.json | base64
Save the encoded output to use later to authenticate your GitLab pipeline.
To create an access key and obtain the secret access key ID:
- Sign in to the AWS Management console and navigate to the IAM dashboard.
- In the navigation pane, choose Users.
- Choose your IAM user name (not the check box).
- Open the Security credentials tab, and then choose Create access key.
- To see the new access key, choose Show.
- To download the key pair, choose Download .csv file. Store this file in a secure location.
Important: This is your only opportunity to view or download the secret access key, and you'll need it later. If you lose it, you'll need to create a new access key.
Set up GitLab
To use our example Flask application, create a new GitLab project and choose Import project during setup. Use the URL https://github.com/coherenceplatformdemos/flask-postgres-employees-demo.git. The example app will be cloned to your GitLab account.
Set up the CI/CD pipeline
In your GitLab project, navigate to Settings, then CI/CD. Expand the Variables section and add the following keys:
COHERENCE_ACCESS_TOKEN: Access token generated in your profileCOHERENCE_APPLICATION: Name of the Coherence applicationCOHERENCE_COLLECTION: Name of the Coherence collectionCOHERENCE_ENVIRONMENT: Name of the Coherence environmentCOHERENCE_SERVICE: Name of the Coherence serviceCOHERENCE_MANAGED_REGISTRY_URL: The URL of the managed registry that was generated by the provisioning process
Also add the following based on which cloud service you use:
GCP_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_KEY: The Base64 string created from the downloaded JSON fileGCP_REGION: GCP regionGCP_PROJECT_ID: The ID of your project
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: Your AWS access key IDAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: Your AWS secret access keyAWS_DEFAULT_REGION: The AWS region of the ECR repository created by Coherence
Sensitive values should be marked as Protected and Masked to help prevent them from being compromised in logs.
Now create your GitLab pipeline by navigating to Build, then Pipeline editor. Either open an existing pipeline or click the Configure pipeline button.
Copy the following into your pipeline file:
stages:
- build
- deploy
variables:
DOCKER_HOST: tcp://docker:2375/
DOCKER_TLS_CERTDIR: ""
# Build image and push to managed artifact registry
build:
stage: build
image: google/cloud-sdk:latest
services:
- docker:dind
before_script:
- echo $GCP_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_KEY | base64 -d > gcloud-service-key.json
- gcloud auth activate-service-account --key-file gcloud-service-key.json
- gcloud auth configure-docker $GCP_REGION --quiet
script:
- docker build -t $COHERENCE_MANAGED_REGISTRY_URL:$CI_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA .
- docker push $COHERENCE_MANAGED_REGISTRY_URL:$CI_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA
# Deploy image using cocli
deploy:
stage: deploy
image: alpine:latest
before_script:
- apk add --no-cache curl jq
- curl -L https://github.com/coherenceplatform/cocli/releases/latest/download/cocli-linux-amd64 -o /usr/local/bin/cocli
- chmod +x /usr/local/bin/cocli
script:
- APP_ID=$(cocli apps list | jq -r ".[] | select(.title==\"$COHERENCE_APPLICATION\") | .id")
- ENV_ID=$(cocli collections list --app_id $APP_ID | jq ".data[] | select(.name == \"$COHERENCE_COLLECTION\") | .latest_infra_config.valid_environments[] | select(.name == \"$COHERENCE_ENVIRONMENT\") | .id")
- echo '{"services":[{"name":"'$COHERENCE_SERVICE'","commit_sha":"'$CI_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA'"}],"configure_infra":false}' > deploy.json
- cocli environments deploy "$ENV_ID" deploy.json
stages:
- build
- deploy
variables:
DOCKER_HOST: tcp://docker:2375/
DOCKER_TLS_CERTDIR: ""
build:
stage: build
image: docker:latest
services:
- docker:dind
before_script:
- apk add --no-cache curl python3 py3-pip
- pip3 install awscli --break-system-packages
- aws configure set aws_access_key_id $AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
- aws configure set aws_secret_access_key $AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
- aws configure set region $AWS_DEFAULT_REGION
# Authenticate with ECR
- aws ecr get-login-password --region $AWS_DEFAULT_REGION | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin $COHERENCE_MANAGED_REGISTRY_URL
script:
- docker build -t $COHERENCE_MANAGED_REGISTRY_URL:$CI_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA .
- docker push $COHERENCE_MANAGED_REGISTRY_URL:$CI_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA
deploy:
stage: deploy
image: alpine:latest
before_script:
- apk add --no-cache curl jq
- curl -L https://github.com/coherenceplatform/cocli/releases/latest/download/cocli-linux-amd64 -o /usr/local/bin/cocli
- chmod +x /usr/local/bin/cocli
script:
- APP_ID=$(cocli apps list | jq -r ".[] | select(.title==\"$COHERENCE_APPLICATION\") | .id")
- ENV_ID=$(cocli collections list --app_id $APP_ID | jq ".data[] | select(.name == \"$COHERENCE_COLLECTION\") | .latest_infra_config.valid_environments[] | select(.name == \"$COHERENCE_ENVIRONMENT\") | .id")
- echo '{"services":[{"name":"'$COHERENCE_SERVICE'","commit_sha":"'$CI_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA'"}],"configure_infra":false}' > deploy.json
- cocli environments deploy "$ENV_ID" deploy.json
This pipeline is set up to build the Docker image and push it to the Coherence-managed Artifact Repository as the first task.
The second task is to deploy the Docker image to the cloud infrastructure using cocli.
Deploy the application
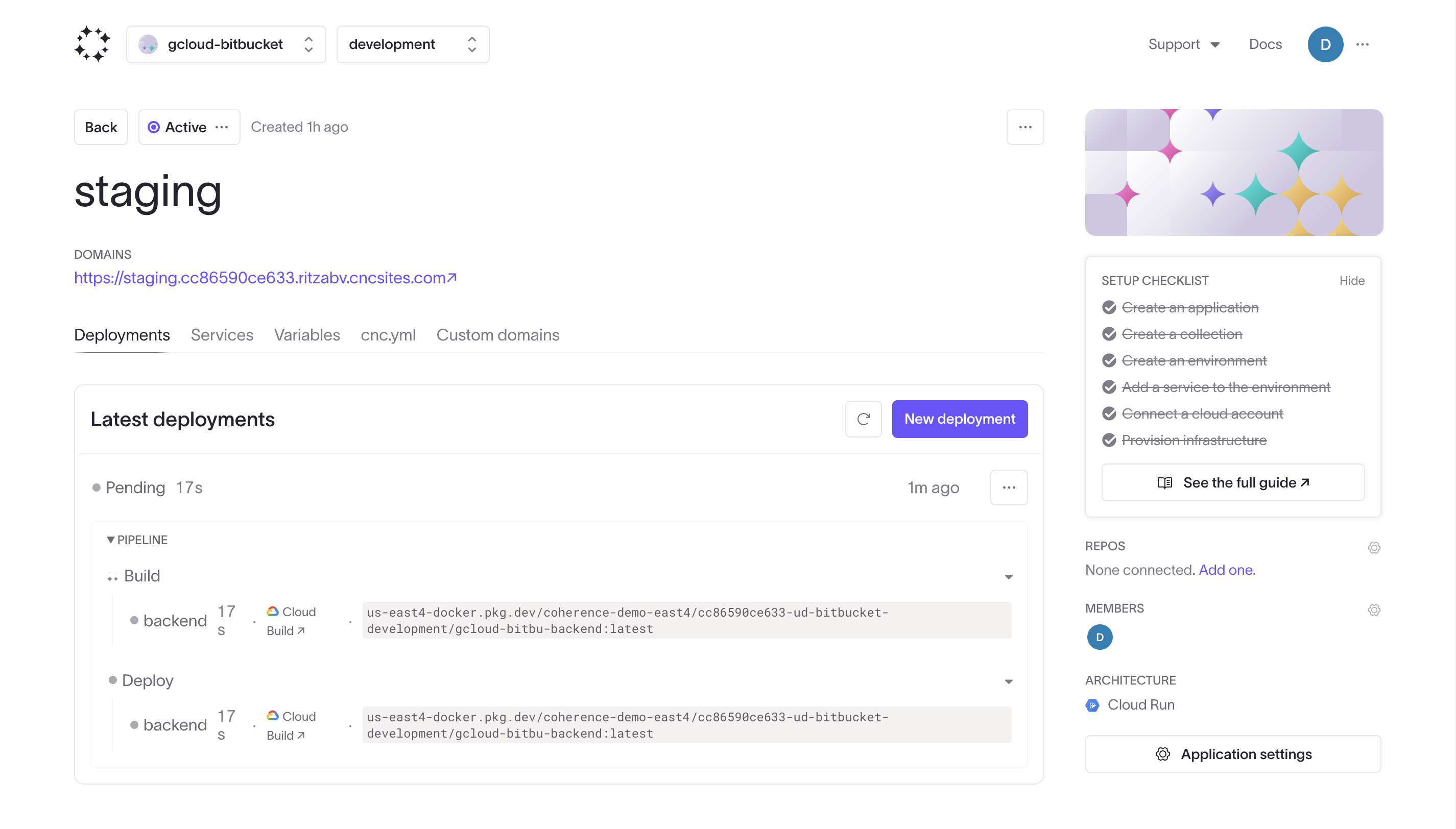
To deploy the application, commit and push your changes to trigger the GitLab pipeline. Once the pipeline completes successfully, Coherence will build and deploy the app automatically. Find the app live at the URL provided in your environment dashboard.
If you followed along with the example project, you will see and be able to use the full-stack employee-management application:
Commit to trigger a new deploy
Once your initial deployment is complete, you can update your application by making changes to your code and pushing them to GitLab. The push will automatically trigger the GitLab pipeline, which will build a new Docker image and push it to your managed registry. Coherence will then deploy this new image to your environment.
You can monitor the progress of your deployment in the Coherence dashboard. Once complete, you'll see your changes reflected in the live application.
To test this process with the example project, open the templates/index.html file and change background-color: rgba(223, 208, 245, 0.98); to background-color: rgba(208, 245, 210, 0.98);. Commit and push this change to trigger a new deployment.
Deploy to multiple environments
You can set up more pipelines for branches in your GitLab repository to deploy to various Coherence environments automatically. Edit the variables in the pipeline file (specifically, ENV_NAME) in a new branch to deploy to the environment of your choice. You can then commit to different branches (for example, develop, staging, and main) to trigger deployments to their corresponding environments in Coherence. Set this up to test in isolated environments and stage releases.