Environment Variables
Coherence provides a robust variable management system that allows you to configure and manage variables for your services. Coherence variables can be used to store sensitive information, such as API keys, database credentials, and other configuration settings.
Team members can easily view and manage variables based on their permissions, at either the collection level or the environment level.
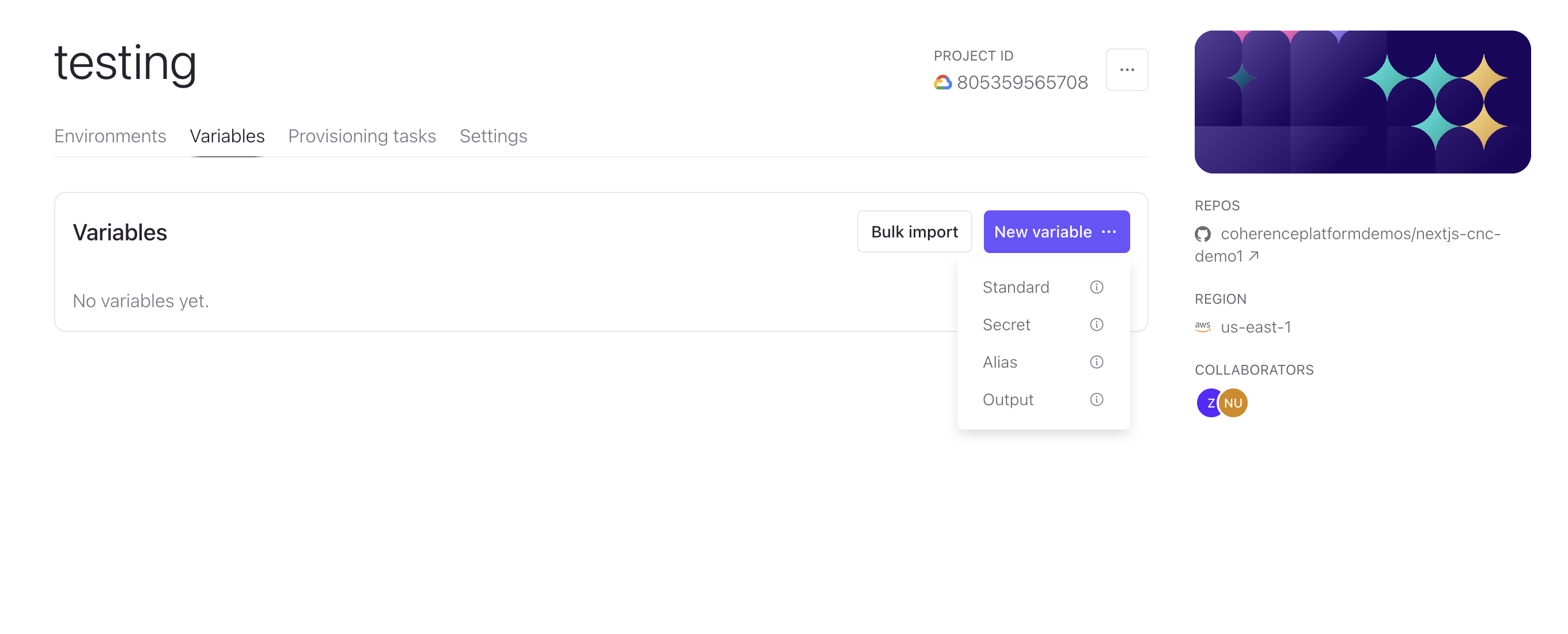
The Coherence UI provides you with flexibility and control over environment configurations by supporting the management of all four variable types:
- Standard
- Secret
- Alias
- Output
Environment inheritance
Variables can be configured in two main areas within the Coherence UI:
- The Variables tab on your collection homepage: These variables will be inherited by all environments within that cloud project (called a "collection"). For example, variables in the "Preview" collection will automatically apply to all branch previews by default.
- The Variables tab on your environment homepage: These variables apply only to the environment for which they are configured. In the Inherited section of this tab, you can override inherited variables using the three-dot menu to the right of each variable name.
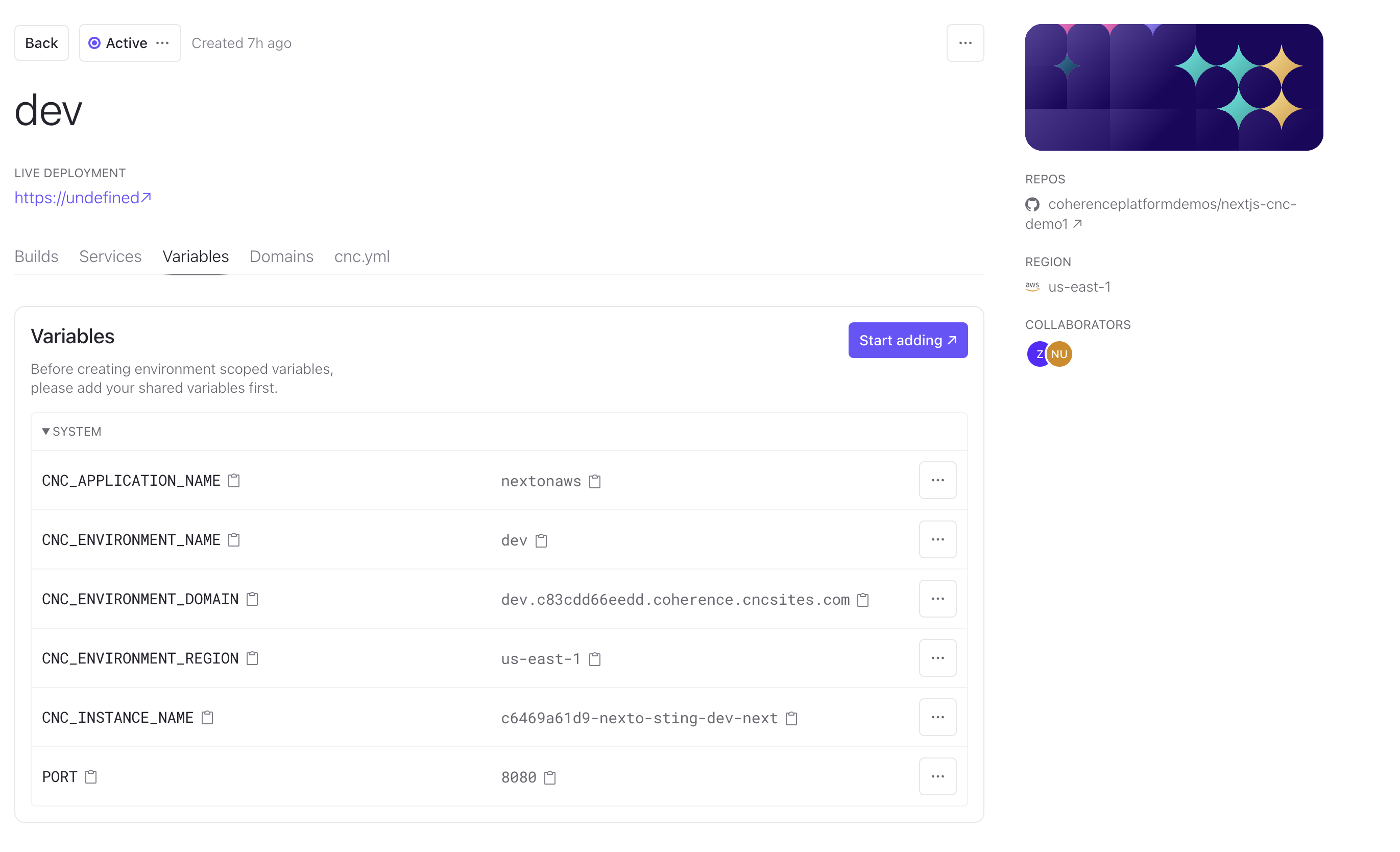
System-managed variables
Coherence also provides system-managed variables for your application, which can be viewed within each environment. These include essential resource variables like DATABASE_URL and REDIS_URL, as well as informational variables such as CNC_ENVIRONMENT_NAME. For more details, refer to the CNC documentation for environment variables.
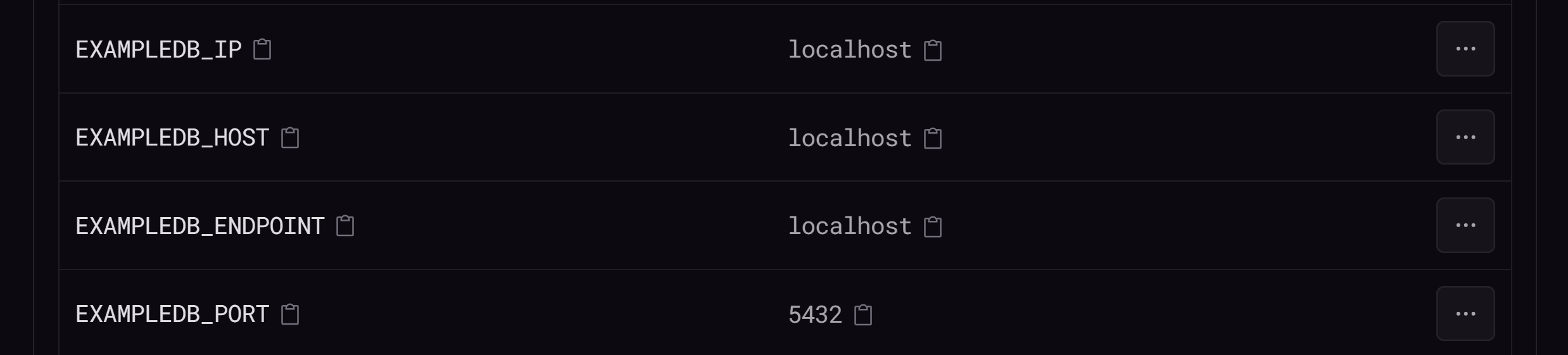
For database services, Coherence will automatically generate the necessary environment variables for your database service once the service has been provisioned. You can view the variables your application requires to connect to your database service in the Variables tab on the environment homepage.
Docker build-args
All environment variables relevant to a service are automatically added as build-args during the docker build process for that service's container.
- To use these variables, be sure to include the
ARGcommands in your Dockerfile, as specified in the Docker documentation.